43 are treasury bills zero coupon bonds
Treasury Bills (T-Bills) - Meaning, Examples, Calculations - WallStreetMojo Treasury bills are a type of zero-coupon security where the central government borrows funds from the individual for a period of 364 days or less. In return, the investors receive interest. These money market instruments provide a return on investment at once, and there is no provision for periodic returns. Advantages and Risks of Zero Coupon Treasury Bonds - Investopedia Zero-coupon U.S. Treasury bonds are also known as Treasury zeros, and they often rise dramatically in price when stock prices fall. Zero-coupon U.S. Treasury bonds can move up significantly when...
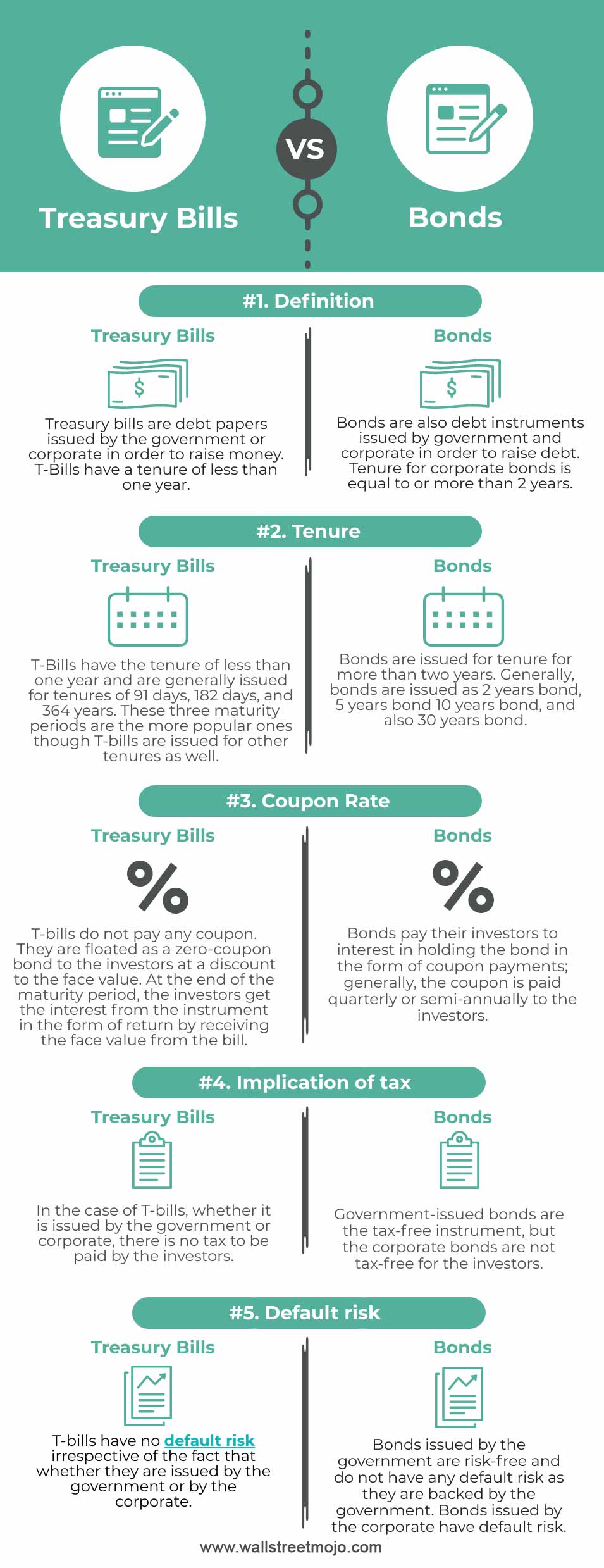
Treasury Bills vs Bonds | Top 5 Differences (with Infographics) Bonds pay interest in the form of a coupon to the investors quarterly or semi-annually. T-bills do not pay any coupon. They are floated as a zero-coupon bond to the investors, issued at discounts, and the investors receive the face value at the end of the tenure, which is the return on their investment. T-bills have no default risk
Are treasury bills zero coupon bonds
What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? Definition, Advantages, Risks 28 Jul 2022 — A zero-coupon bond doesn't pay periodic interest, but instead sells at a deep discount, paying its full face value at maturity. US Treasury Bonds - Fidelity The coupon rate is fixed at the time of issuance and is paid every six months. Other Treasury securities, such as Treasury bills (which have maturities of one year or less) or zero-coupon bonds, do not pay a regular coupon. Instead, they are sold at a discount to their face (or par) value; investors receive the full face value at maturity ... Treasury Yield: What It Is and Factors That Affect It May 25, 2022 · Treasury yield is the return on investment, expressed as a percentage, on the U.S. government's debt obligations. Looked at another way, the Treasury yield is the interest rate that the U.S ...
Are treasury bills zero coupon bonds. What is Treasury Bill (T-bill)? - Indian Economy Treasury bills are presently issued in three maturities, namely, 91 day, 182 day and 364 day. Treasury bills are zero coupon securities and pay no interest. Rather, they are issued at a discount (at a reduced amount) and redeemed (given back money) at the face value at maturity. What Are Singapore Treasury Bills and Are They a Good Investment? Sep 30, 2022 · T-bills have an AAA credit rating with the backing of the Singapore Government, as well as short maturity periods of six months to one year. You can invest with cash, CPF or SRS funds without an overall limit, and — unlike with SGS bonds, which pay investors in coupons — receive the full value upon maturity. Interest Rate Statistics | U.S. Department of the Treasury Oct 11, 2022 · NOTICE: See Developer Notice on changes to the XML data feeds. Daily Treasury PAR Yield Curve Rates This par yield curve, which relates the par yield on a security to its time to maturity, is based on the closing market bid prices on the most recently auctioned Treasury securities in the over-the-counter market. The par yields are derived from input market prices, which are indicative ... Can you lose money on Treasury notes? | Note Brokering Treasury bills are not like coupon bonds that pay interest in accruals. What are Treasury bills example? Treasury bills are zero-coupon securities and do not pay interest. They are issued at a discount and are redeemed at face value at maturity. For example, a 91-day treasury bill of Rs. 100 / - (nominal value) can be issued for example Rs. ...
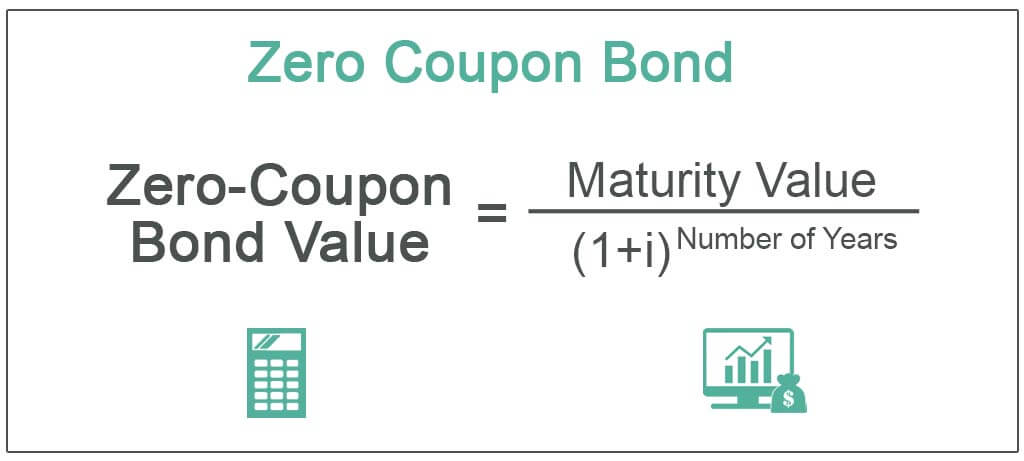
Zero-Coupon Bonds: Characteristics and Examples - Wall Street Prep U.S. Treasury Bills (or T-Bills) are short-term zero-coupon bonds (< 1 year) issued by the U.S. government. Learn More → Zero Coupon Bond (SEC) Zero-Coupon Bond Price Formula To calculate the price of a zero-coupon bond - i.e. the present value (PV) - the first step is to find the bond's future value (FV), which is most often $1,000. Should You Buy Treasuries? - Forbes The shortest U.S. bonds, T-bills, are sold at auction at a discount to the face value (par). Bills mature at par and don't pay interest. Treasury notes and bonds pay interest every six months. HM Treasury - GOV.UK HM Treasury is the government’s economic and finance ministry, maintaining control over public spending, setting the direction of the UK’s economic policy and working to achieve strong and ... What's the difference between a zero-coupon bond and a Treasury bill ... T-bills are also called as zero coupon bond, which is issued at discount. T bills are short term instruments issued within one year. 91 days, 182 days, 364 days are the examples of maturity period. T-bills are issued by goverment of any country. One point to remember
Understanding Zero Coupon Bonds - Part One - The Balance Zero coupon bonds generally come in maturities from one to 40 years. The U.S. Treasury issues range from six months to 30 years and are the most popular ones, along with municipalities and corporations. 1. Here are some general characteristics of zero coupon bonds: You must pay tax on interest annually even though you don't receive it until ... Understanding Pricing and Interest Rates — TreasuryDirect The formula shows that the bill sells for $999.27, giving you a discount of $0.73. Bonds and Notes. Bonds are long-term securities that mature in 20 or 30 years. Notes are relatively short or medium-term securities that mature in 2, 3, 5, 7, or 10 years. Both bonds and notes pay interest every six months. Treasury Bills - Types, Features and Advantages of Government ... - Groww Treasury bills are zero-coupon securities, issued at a discount to investors. Hence, total returns generated by such instruments remain constant through the tenure of bond, irrespective of economic conditions and business cycle fluctuations. Treasury Bills - Guide to Understanding How T-Bills Work T-bills, T-notes, and T-bonds are fixed-income investments issued by the US Department of the Treasury when the government needs to borrow money. They are all commonly referred to as "Treasuries." T-Bills Treasury bills have a maturity of one year or less, and they do not pay interest before the expiry of the maturity period.
Zero-coupon bond - Wikipedia A zero coupon bond (also discount bond or deep discount bond) is a bond in which the face value is repaid at the time of maturity. [1] Unlike regular bonds, it does not make periodic interest payments or have so-called coupons, hence the term zero-coupon bond. When the bond reaches maturity, its investor receives its par (or face) value.
14.3 Accounting for Zero-Coupon Bonds - Financial Accounting Figure 14.9 December 31, Year One—Interest on Zero-Coupon Bond at 6 Percent Rate 3. The compounding of this interest raises the principal by $1,068 from $17,800 to $18,868. The balances to be reported in the financial statements at the end of Year One are as follows: Year One—Interest Expense (Income Statement) $1,068.
What's the difference between a zero-coupon bond ... - Quora T-bills do not pay any coupon. They are floated as a zero-coupon bond to the investors, they are issued at discounts, and the investors receive the face value ...
United States Treasury security - Wikipedia Treasury bills (T-bills) are zero-coupon bonds that mature in one year or less. They are bought at a discount of the par value and, instead of paying a coupon interest, are eventually redeemed at that par value to create a positive yield to maturity.
Treasury Bills vs. Bonds: What's the Difference? - SmartAsset Treasury Bills vs. Savings Bonds. Another common type of bond is the U.S. savings bond. Like T-bills and T-bonds, savings bonds are issued by the Treasury Department to help fund government operations, making them reliable but not lucrative investments. However, unlike T-bills and T-bonds, savings bonds cannot be bought and sold on secondary ...
A guide to US Treasuries - E-Trade Separate Trading of Registered Interest and Principal of Securities (STRIPS): Treasury STRIPS, also known as zero-coupon Treasuries, let investors hold and trade the interest and principal of certain T-notes and bonds as separate securities.
are also called zero coupon bonds. - Byju's are also called zero coupon bonds. The correct option is C. Treasury bills (c) Treasury bills. Explanation: Treasury bills are money market instruments provided by the Government of India as a promissory note with ensured reimbursement on a specific date in the future. Assets gathered through such tools are ordinarily used to meet momentary necessities or for short-term use requirements of the ...
Treasury Bills — TreasuryDirect Treasury Marketable Securities Treasury Bills Treasury Bills We sell Treasury Bills (Bills) for terms ranging from four weeks to 52 weeks. Bills are sold at a discount or at par (face value). When the bill matures, you are paid its face value. You can hold a bill until it matures or sell it before it matures.
Treasury bills are also known as Zero Coupon Bonds ... - Toppr Treasury bills are also known as Zero Coupon Bonds that are available for a minimum of and in multiples thereof. A treasury bill is basically an instrument ...
What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? - Investopedia May 31, 2022 · Zero-Coupon Bond: A zero-coupon bond is a debt security that doesn't pay interest (a coupon) but is traded at a deep discount, rendering profit at maturity when the bond is redeemed for its full ...
Zero Coupon Bonds- Taxability Under Income Tax Act, 1961 - TaxWink Zero Coupon Bonds assures a fixed maturity amount after a certain period. Therefore, the investors who have want to get a fixed return in future with less market risk should go for these bonds. Even if you are an aggressive investor and always hunting for good stocks, you may still invest in these bonds to balance your portfolio.
The One-Minute Guide to Zero Coupon Bonds | FINRA.org Instead of getting interest payments, with a zero you buy the bond at a discount from the face value of the bond, and are paid the face amount when the bond matures. For example, you might pay $3,500 to purchase a 20-year zero-coupon bond with a face value of $10,000. After 20 years, the issuer of the bond pays you $10,000.
Treasury Bills vs Bonds | Top 5 Best Differences (With Infographics) Treasury bond The bond is sold at their face value and has a fixed interest rate which is paid once every six months. Some of the key bonds are Municipal bonds, Governments bonds, corporate bonds, Zero Coupons bonds, etc. Bonds also called fixed-income instruments. Example:
Treasury Coupon Issues and Corporate Bond Yield Curves Treasury Coupon Issues Learn about the Treasury Yield Curves for Nominal and Real Coupon Issues (TNC and TRC yield curves) and The Treasury Breakeven Inflation Curve (TBI curve). Corporate Bond Yield Curve Papers and Data Learn about the corporate bond yield curve, and how it relates to the Pension Protection Act, by downloading these papers.
Treasury Coupon Issues | U.S. Department of the Treasury Treasury Coupon Issues The Yield Curve for Treasury Nominal Coupon Issues (TNC yield curve) is derived from Treasury nominal notes and bonds. The Yield Curve for Treasury Real Coupon Issues (TRC yield curve) is derived from Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS).
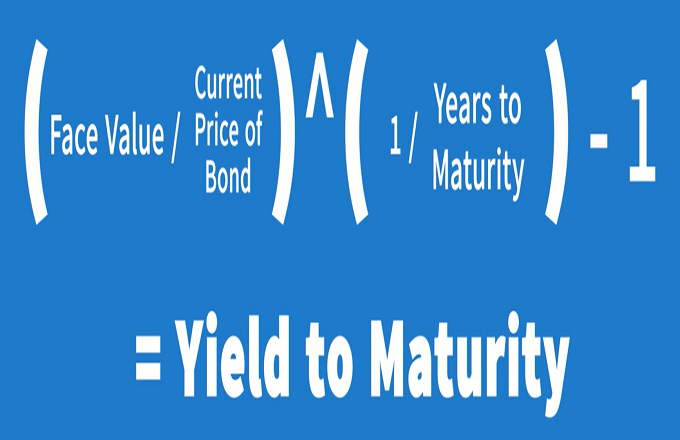
What Are Treasury Bills (T-Bills) and How Do They Work? - Investopedia T-bills are zero-coupon bonds that are usually sold at a discount and the difference between the purchase price and the par amount is your accrued interest. How Can I Buy a Treasury Bill? U.S....
Zero Coupon Bond - Investor.gov Zero coupon bonds are bonds that do not pay interest during the life of the bonds. Instead, investors buy zero coupon bonds at a deep discount from their face value, which is the amount the investor will receive when the bond "matures" or comes due.
Zero-Coupon Bond - Definition, How It Works, Formula It is also called a pure discount bond or deep discount bond. U.S. Treasury bills are an example of a zero-coupon bond. Summary A zero-coupon bond is a bond that pays no interest. The bond trades at a discount to its face value. Reinvestment risk is not relevant for zero-coupon bonds, but interest rate risk is relevant for the bonds.
Treasury Yield: What It Is and Factors That Affect It May 25, 2022 · Treasury yield is the return on investment, expressed as a percentage, on the U.S. government's debt obligations. Looked at another way, the Treasury yield is the interest rate that the U.S ...
US Treasury Bonds - Fidelity The coupon rate is fixed at the time of issuance and is paid every six months. Other Treasury securities, such as Treasury bills (which have maturities of one year or less) or zero-coupon bonds, do not pay a regular coupon. Instead, they are sold at a discount to their face (or par) value; investors receive the full face value at maturity ...
What Is a Zero-Coupon Bond? Definition, Advantages, Risks 28 Jul 2022 — A zero-coupon bond doesn't pay periodic interest, but instead sells at a deep discount, paying its full face value at maturity.
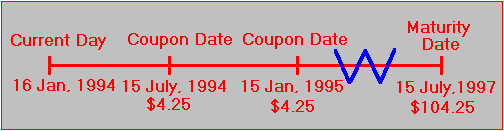




/-1000-denomination-us-savings-bonds-172745598-cdf4a528ed824cc58b81f0531660e9c9.jpg)






















Post a Comment for "43 are treasury bills zero coupon bonds"